

Molecules lack symmetry and have a polar bond (also called a covalent bond), then it is a polar molecule.

Some of the examples can be HN, HF, H2O, NH3, CH3COOH The Molecule has a hydrogen bond, not a covalent bond, then it is a polar molecule.The difference is less than 0.5 so this molecule is nonpolar or can be classified as a very slightly polar. It is a non-symmetric molecule where electronegativity of Br is 2.8 and that of Cl is 3.0. One example of this condition can be BrCl. Not necessarily! In such cases, the electronegativity difference needs to be checked once. Here, a question arises: What if a molecule lacks symmetry, is it always going to be polar? You can check out the reason for the non-polarity of CS2. This means that electrons are similarly arranged throughout the structure. Molecules that have symmetry in its structure.Molecules containing only carbon and hydrogen atoms ie hydrocarbons.Some examples can be N2, F2, H2, He, Ne, Ar, Xe. The Molecules that are made of the same element are generally seen nonpolar.Points to determine if the molecule is polar or nonpolar? Polar molecules are usually seen with hydrogen bond The electronegativity difference should be between 0.5 to 1.6įormation of a covalent bond is essential The electronegativity difference between the two hydrogen atoms is 0 which is less than 0.5. The electronegativity difference should be less than 0.5 Major differences between Polar and Nonpolar Molecules? Nonpolar Molecules Such a condition leads to the formation of no poles and ultimately becoming a nonpolar molecule. This means there will be no difference in charge distribution on the surface of this molecule. It means both the atoms will pull equally on the shared pair of electrons. You can also say, both the atoms are strongly going to attract the shared pair of electrons in the covalent bond.įor H2 atom, electronegativity will be the same for both the atoms.
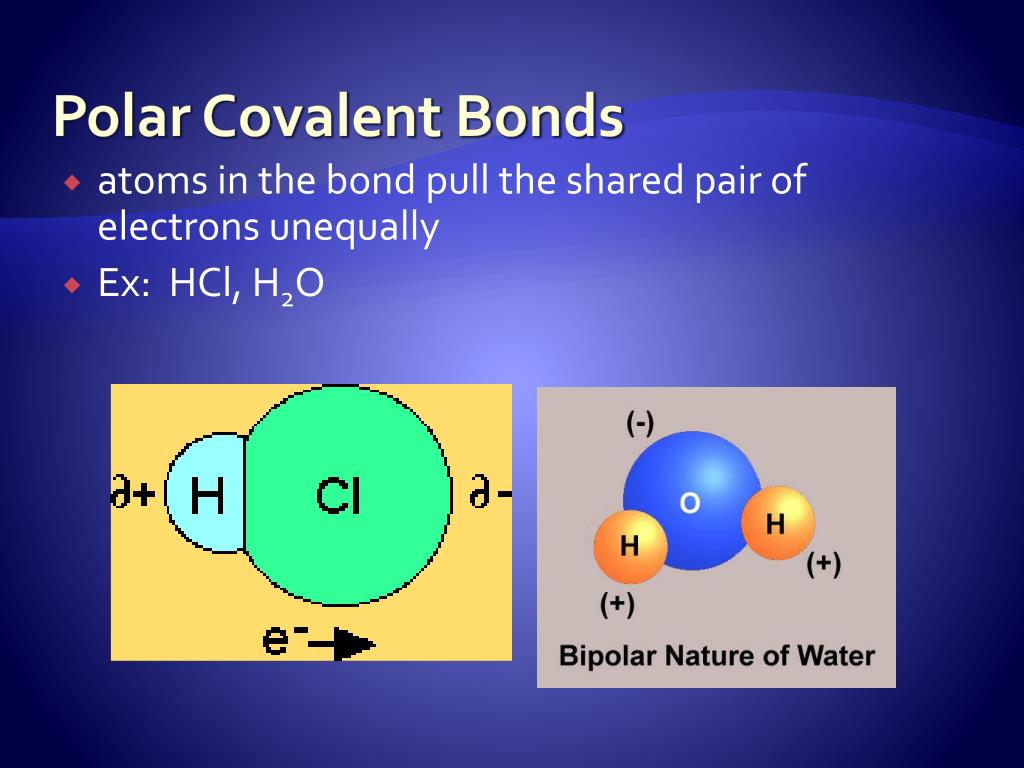
When it comes in contact with another hydrogen (H) atom, both the valence electrons pair up to stabilize each other’s structure. Single hydrogen (H) atom has only one valence electron in its outermost shell.Īlso, it needs only one electron to stabilize itself. Hydrogen gas is one of the simplest nonpolar covalent molecules. Why is hydrogen gas (H2) molecule nonpolar in nature? They dissociate to form ions in the water (means they dissolve in the water) They have lower melting and boiling points than the polar molecules They have high melting and boiling points than the nonpolar molecules They conduct electricity when present in the aqueous solution They have weaker forces of attraction than the Van der Waal’s They have stronger forces of attraction than the Van der Waal’s forces between the molecules Let us discuss the abilities of both the molecules separately, in a table Polar Molecules (Covalent bonds) This shared pair of electrons form a covalent bond that stabilizes both the attractive and repulsive forces between the atoms. The electrons present in the outermost orbit can participate only, to bond with an electron of another atom. Like our solar system, electrons move in their respective orbits within an atom. This form nonpolar covalent bond and nonpolar molecule. Oppositely, when an equal number of electrons are shared between the atoms, no partial charge is developed. In a case where electronegativities of two atoms are not the same, an equal number of electrons are not shared and a partial charge is developed. It is a phenomenon by which an atom attracts a shared pair of electrons towards itself.

The elements exhibit the tendency of polarity because of electronegativity. Here, the electronegativities of participating atoms are the same. Whereas, nonpolar molecules are those where an equal number of electrons are shared between the interacting atoms. This creates a difference in the electronegativity of participating atoms. \).Polar molecules are those where an unequal number of electrons are shared between their bonded atoms.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
